The Role of Big Data in Banking
Big data has become a critical asset in the banking industry, offering unprecedented insights and capabilities that transform operations, customer service, and risk management. As banks gather vast amounts of data from various sources, the ability to analyze and leverage this information becomes increasingly vital. This article explores the role of big data in banking, focusing on how it enhances decision-making, customer experience, and overall efficiency.

The Role of Big Data in Banking
Enhancing Customer Experience with Big Data
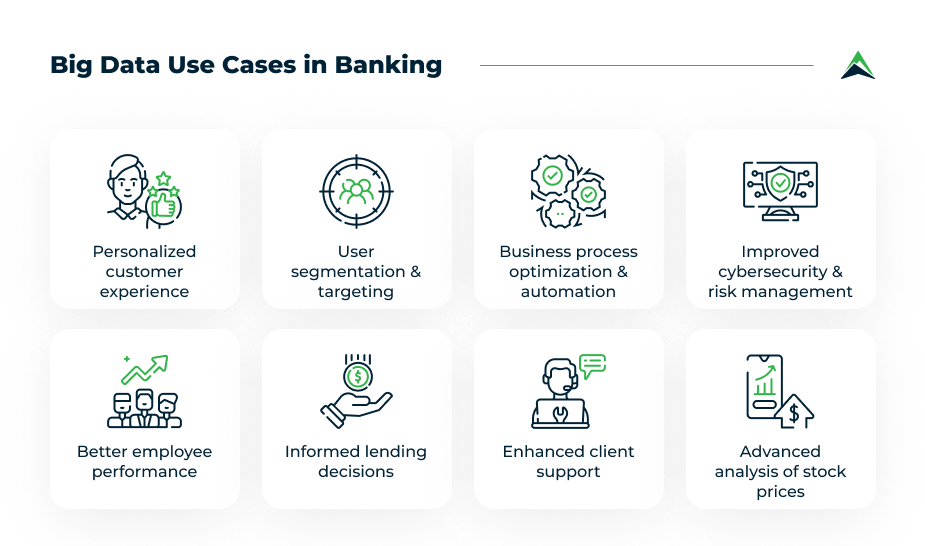
Big data plays a pivotal role in personalizing customer experiences within the banking sector. By analyzing customer data, banks can better understand individual preferences, behaviors, and needs. This information allows banks to offer tailored services, personalized product recommendations, and targeted marketing efforts.
For example, through big data analytics, banks can track customer spending patterns and identify trends. Therefore, they can offer customized financial advice or product suggestions that align with the customer’s lifestyle. Moreover, big data enables banks to anticipate customer needs, providing proactive solutions that enhance satisfaction and loyalty.
Furthermore, big data facilitates real-time customer support by enabling banks to monitor interactions and resolve issues promptly. By analyzing data from customer inquiries, banks can identify common problems and implement solutions that improve the overall customer experience. Hence, big data is instrumental in creating a more responsive and customer-centric banking environment.
Improving Risk Management and Fraud Detection
Risk management is another area where big data significantly impacts banking. Banks face various risks, including credit risk, market risk, and operational risk. Big data analytics allows banks to assess and mitigate these risks more effectively.
For instance, by analyzing historical data, banks can identify patterns that indicate potential credit risks. This analysis enables banks to make informed decisions when approving loans or extending credit, reducing the likelihood of defaults. Additionally, big data helps banks predict market fluctuations and adjust their strategies accordingly, thus minimizing financial losses.
Moreover, fraud detection is a critical aspect of risk management where big data proves invaluable. By analyzing transaction data in real-time, banks can detect unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities. Furthermore, big data enables the use of advanced machine learning algorithms that continuously improve fraud detection accuracy. As a result, banks can respond to potential threats more quickly, protecting both their assets and their customers.
Optimizing Decision-Making Processes
Big data enhances decision-making processes within the banking sector by providing comprehensive insights and predictive analytics. Banks can leverage big data to inform strategic decisions, such as entering new markets, launching new products, or adjusting pricing strategies.
For example, predictive analytics powered by big data can help banks forecast market trends and customer demand. This foresight allows banks to allocate resources more efficiently and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Additionally, big data enables banks to conduct more accurate financial modeling, supporting better investment decisions and portfolio management.
Furthermore, big data allows for continuous monitoring and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs). By tracking these metrics in real-time, banks can quickly identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions. Therefore, big data not only supports more informed decision-making but also enhances agility and responsiveness in a rapidly changing financial landscape.
Streamlining Operations and Reducing Costs
In addition to improving customer experience and decision-making, big data also contributes to streamlining operations and reducing costs in banking. By automating data-driven processes, banks can achieve greater efficiency and reduce operational expenses.
For instance, big data analytics can optimize back-office functions such as transaction processing, compliance monitoring, and reporting. Automating these processes reduces the time and resources required to complete them, resulting in significant cost savings. Moreover, big data enables more efficient resource allocation by identifying areas where operations can be streamlined or automated.
Additionally, big data helps banks optimize their workforce by analyzing employee performance data. This analysis can identify areas where training or additional support is needed, leading to a more productive and efficient workforce. Thus, big data contributes to overall operational efficiency, enabling banks to operate more cost-effectively.
Conclusion
Big data plays a transformative role in the banking industry, driving improvements in customer experience, risk management, decision-making, and operational efficiency. By leveraging the power of big data, banks can offer personalized services, detect and mitigate risks more effectively, and make more informed strategic decisions. Furthermore, big data enables banks to streamline operations and reduce costs, contributing to a more efficient and competitive financial sector.
In summary, the integration of big data into banking operations is not just a trend but a necessity in today’s data-driven world. Therefore, banks that embrace big data will be better positioned to meet the evolving needs of their customers and succeed in an increasingly complex financial landscape.