The Impact of Big Data on Modern Farming
The agricultural sector is experiencing a transformation as big data technologies become integral to farming practices. Big data refers to the vast volumes of data generated from various sources, such as sensors, satellite imagery, and farm equipment. When analyzed, this data provides insights that help farmers make informed decisions, optimize operations, and ultimately increase productivity. This article explores the impact of big data on modern farming, highlighting its benefits, challenges, and future potential.
Optimizing Crop Yields Through Data-Driven Decisions
One of the most significant impacts of big data on farming is its ability to optimize crop yields. By collecting data on soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop performance, farmers can make precise decisions about planting, fertilizing, and irrigating. For example, soil sensors can measure moisture levels and nutrient content, allowing farmers to apply water and fertilizers only where needed. This targeted approach reduces waste, lowers costs, and boosts crop yields.
Additionally, big data enables predictive analytics, which helps farmers anticipate and mitigate potential issues before they affect the crop. By analyzing historical data and current conditions, farmers can predict pest infestations, disease outbreaks, and adverse weather events. This foresight allows for timely interventions, reducing the risk of crop loss.
Discovering a Comprehensive Online Casino Platform
Finding a reliable online casino can be challenging. A comprehensive platform offers a variety of games and secure transactions. For a well-rounded online casino experience, check out kingjohnnie casino. This site provides numerous gaming options and a safe environment for players. The variety of games ensures entertainment for all.
Enhancing Efficiency with Precision Agriculture
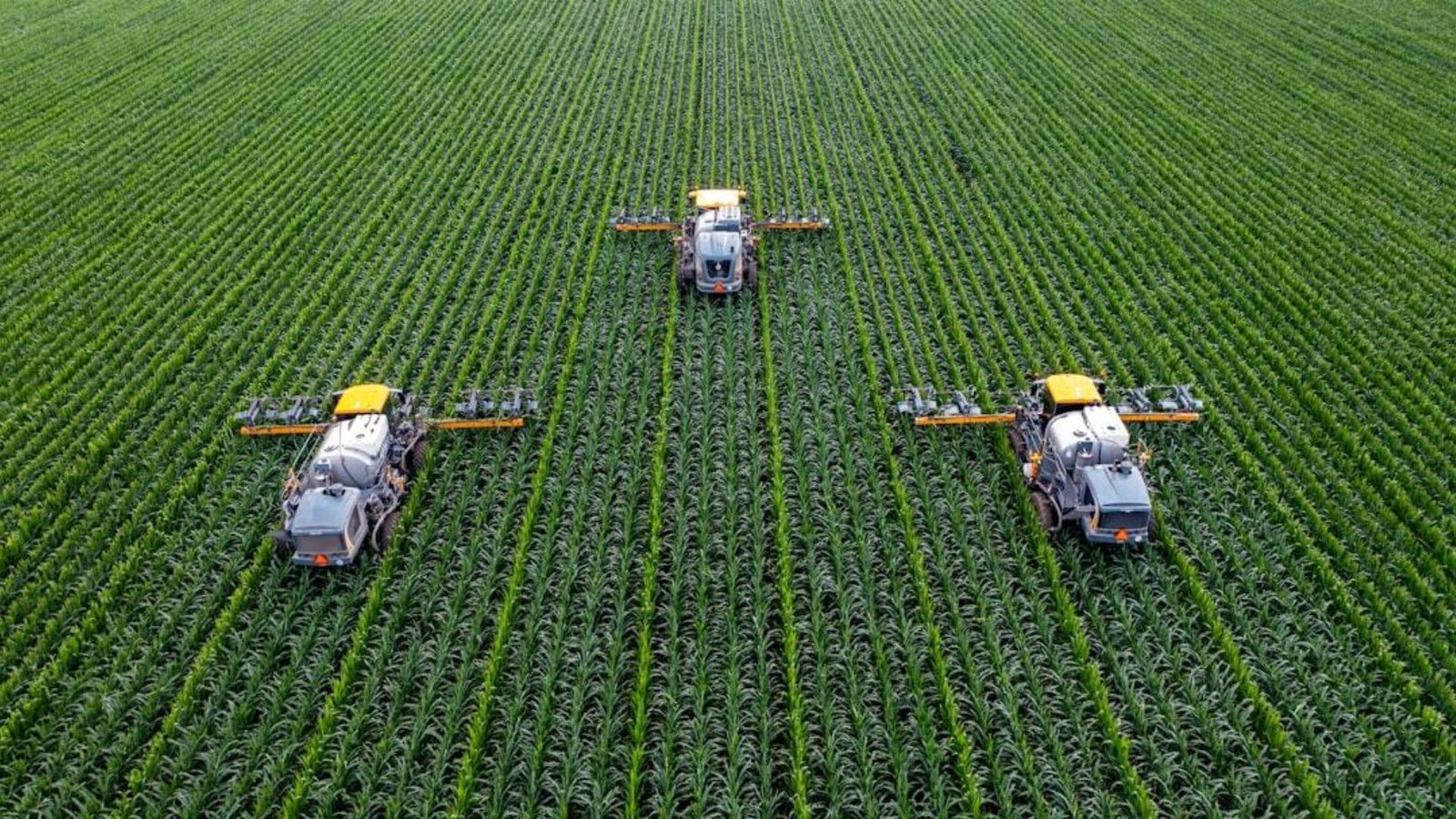
Precision agriculture, a farming management concept that uses big data to ensure crops and soil receive exactly what they need for optimum health and productivity, is another area where big data is making a significant impact. This approach minimizes the use of inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, thereby reducing environmental impact while maximizing yield.
Farm equipment outfitted with GPS and IoT devices collects data in real-time, enabling farmers to monitor field conditions with unparalleled accuracy. For instance, tractors equipped with GPS can plant seeds at exact locations, ensuring uniformity and reducing waste. Drones and satellite imagery provide aerial views of fields, helping farmers monitor crop health and identify areas that need attention.
Improving Supply Chain Management
Big data is also transforming supply chain management in agriculture. By tracking crops from the field to the market, farmers and suppliers can ensure that products reach consumers in optimal condition. Data analytics can help predict demand, allowing farmers to plan harvests and reduce waste. Additionally, data from the supply chain can improve traceability, ensuring that consumers receive safe and high-quality products.
For example, blockchain technology, when integrated with big data, can track every stage of the supply chain, from the farm to the consumer. This transparency helps in identifying and resolving issues quickly, such as contamination or spoilage, thus maintaining the integrity of the supply chain.

www.leroijohnny1.net/fr
2buntu.com appears to be a website focused on Ubuntu or Linux-related topics, offering resources and information for users. While individuals engage with open-source technology and software, some might also enjoy online entertainment during their leisure time. For those interested in exploring online gaming platforms, more information can be found at www.leroijohnny1.net/fr. This resource offers a variety of online casino games for adults seeking a different form of digital engagement.
Challenges in Implementing Big Data in Farming
While the benefits of big data in farming are clear, there are also challenges to its implementation. One of the primary challenges is the cost of technology. Small-scale farmers, particularly in developing countries, may find it difficult to invest in the necessary equipment and software. Furthermore, there is a need for expertise in data analysis, which can be a barrier for farmers who are not familiar with digital tools.
Another challenge is data security and privacy. With the increasing reliance on digital tools, there is a risk of data breaches that could compromise sensitive information about farm operations. Farmers must ensure that they use secure platforms and follow best practices to protect their data.
Take a Fun Break from Tech
After exploring Linux tips and tech insights, users can relax and enjoy interactive online entertainment by visiting stellarspins Login, offering a fun and engaging digital experience.
The Future of Big Data in Farming
The future of big data in farming looks promising as technology continues to advance. Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to play a more significant role in analyzing agricultural data, providing even more accurate predictions and insights. Moreover, as the technology becomes more affordable and accessible, more farmers will be able to adopt big data solutions.
Collaboration between technology providers, governments, and farmers will be crucial in overcoming the challenges associated with big data. By working together, these stakeholders can develop affordable solutions, provide training for farmers, and establish regulations to protect data privacy.
Exploring Tech and Entertainment Synergies
At 2buntu, we’re passionate about open-source solutions and the evolving digital landscape. As the tech world continues to grow, so do digital entertainment options, including online slots in canada. These platforms showcase how technology enhances user experiences in real-time gaming environments. It’s a fascinating intersection of code and creativity that keeps evolving with every click.
Conclusion
In conclusion, big data is revolutionizing modern farming by optimizing crop yields, enhancing efficiency, and improving supply chain management. While challenges such as cost and data security remain, the potential benefits of big data in agriculture are immense. As technology continues to evolve, big data will play an increasingly vital role in ensuring the sustainability and productivity of global agriculture.